Prescribed events are used in Scrum to create regularity and to minimize the need for meetings not defined in Scrum. All events are time-boxed events, such that every event has a maximum duration. Once a Sprint begins, its duration is fixed and cannot be shortened or lengthened. The remaining events may end whenever the purpose of the event is achieved as long as they don’t go over their time box, ensuring an appropriate amount of time is spent without allowing waste in the process.
Other than the Sprint itself, which is a container for all other events, each event in Scrum is a formal opportunity to inspect and adapt something. These events are specifically designed to enable critical transparency and inspection. Failure to include any of these events results in reduced transparency and is a lost opportunity to inspect and adapt.
The Sprint
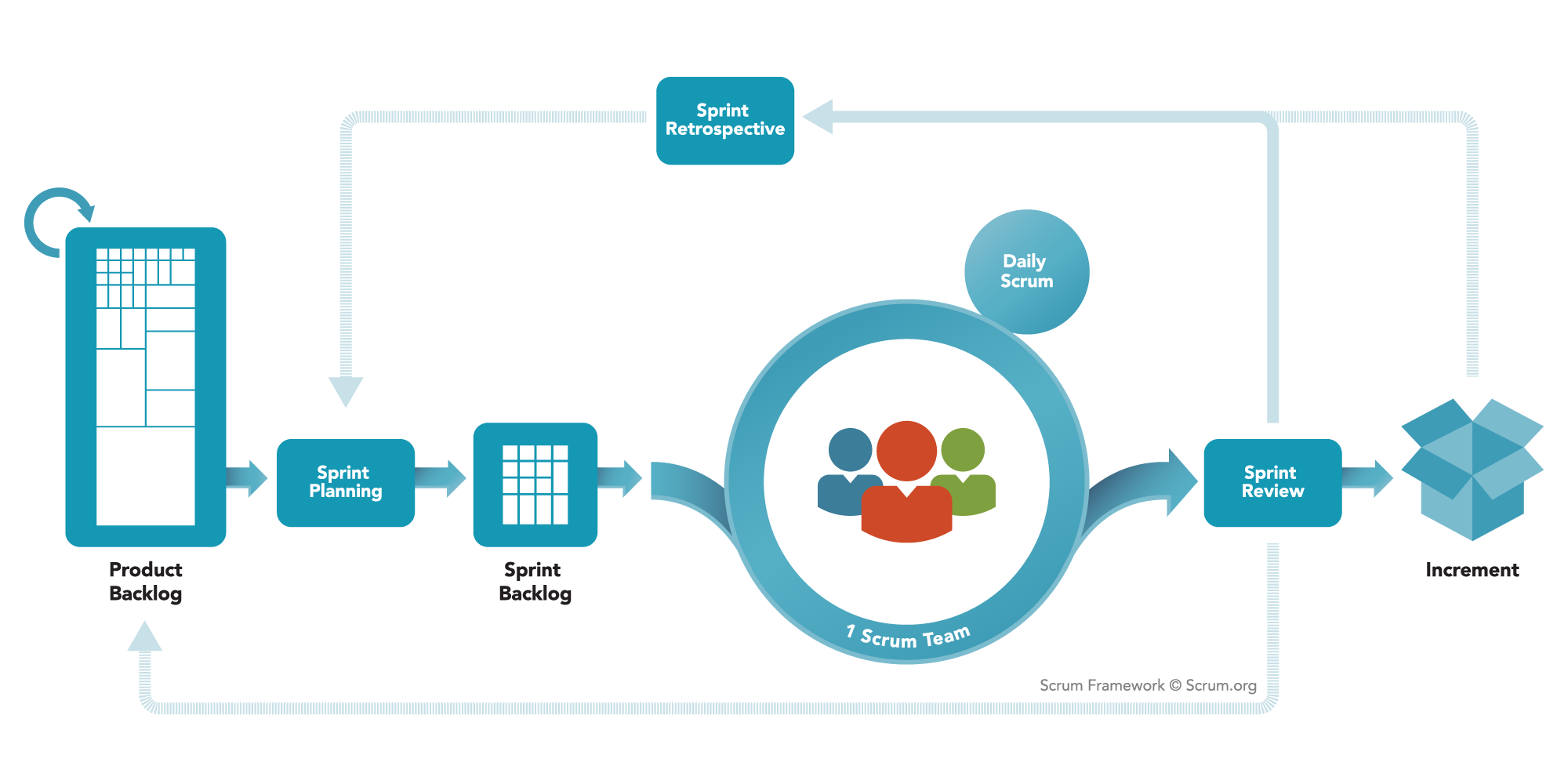
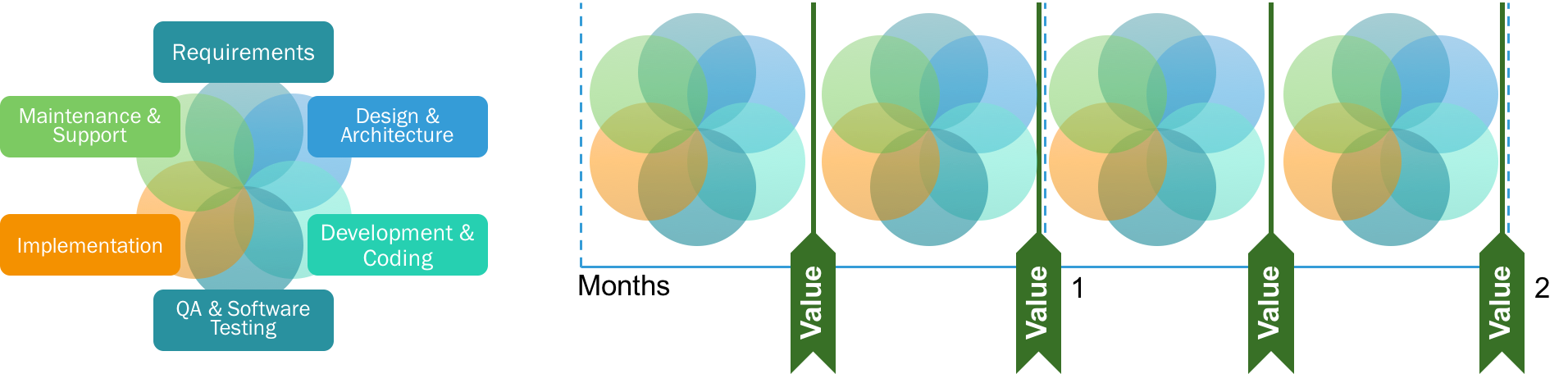
The heart of Scrum is a Sprint, a time-box of one month or less during which a “Done”, useable, and potentially releasable product Increment is created. Sprints best have consistent durations throughout a development effort. A new Sprint starts immediately after the conclusion of the previous Sprint.
Sprints contain and consist of the Sprint Planning, Daily Scrums, the development work, the Sprint Review, and the Sprint Retrospective.
Each Sprint may be considered a project with no more than a one-month horizon. Like projects, Sprints are used to accomplish something. Each Sprint has a definition of what is to be built, a design and flexible plan that will guide building it, the work, and the resultant product.
Sprint Goal
The Sprint Goal is an objective set for the Sprint that can be met through the implementation of Product Backlog items. It provides guidance to the Development Team on why it is building the Increment. It is created during the Sprint Planning meeting. The Sprint Goal gives the Development Team some flexibility regarding the functionality implemented within the Sprint. The selected Product Backlog items deliver one coherent function, which can be the Sprint Goal. The Sprint Goal can be any other coherence that causes the Development Team to work together rather than on separate initiatives.
As the Development Team works, it keeps the Sprint Goal in mind. In order to satisfy the Sprint Goal, it implements the functionality and technology. If the work turns out to be different than the Development Team expected, they collaborate with the Product Owner to negotiate the scope of Sprint Backlog within the Sprint.
Sprint Planning Meeting
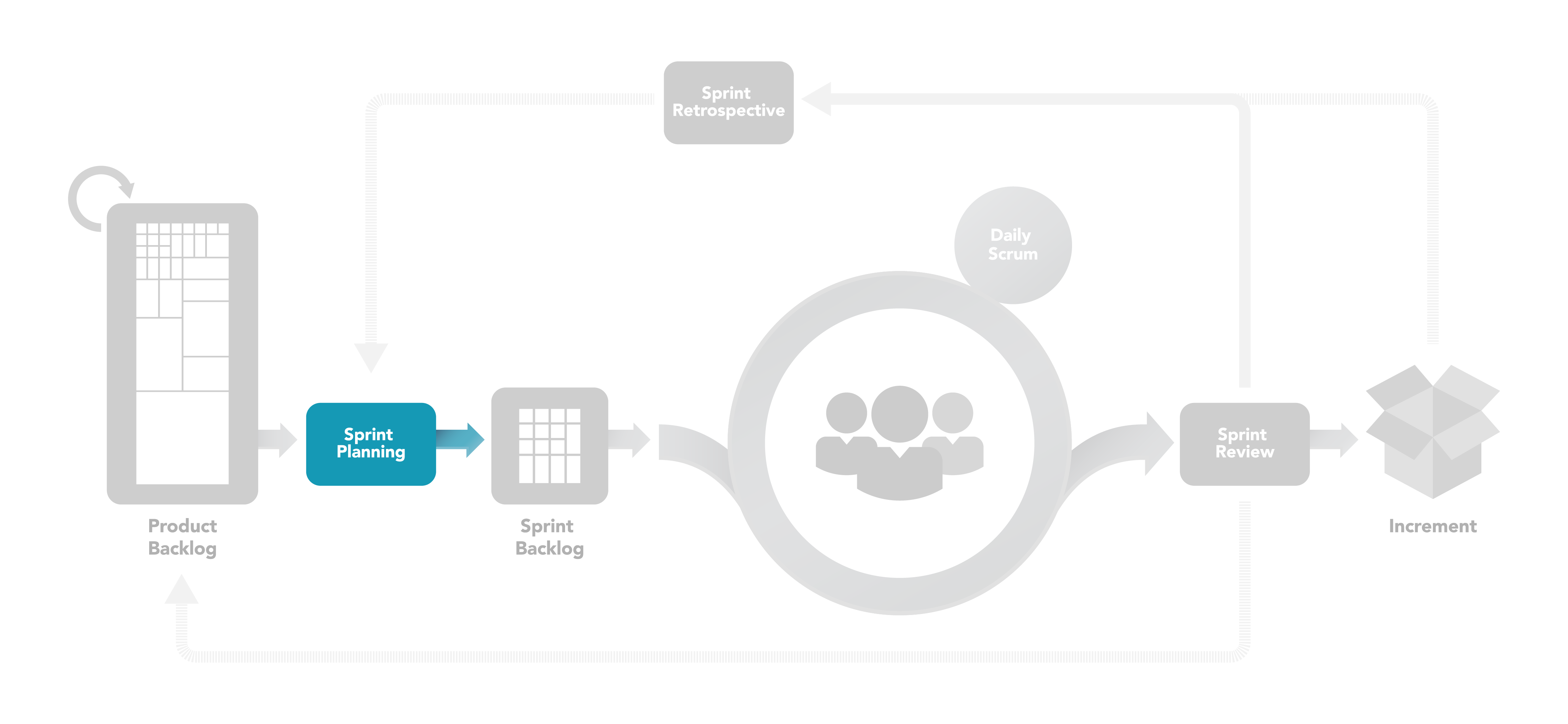
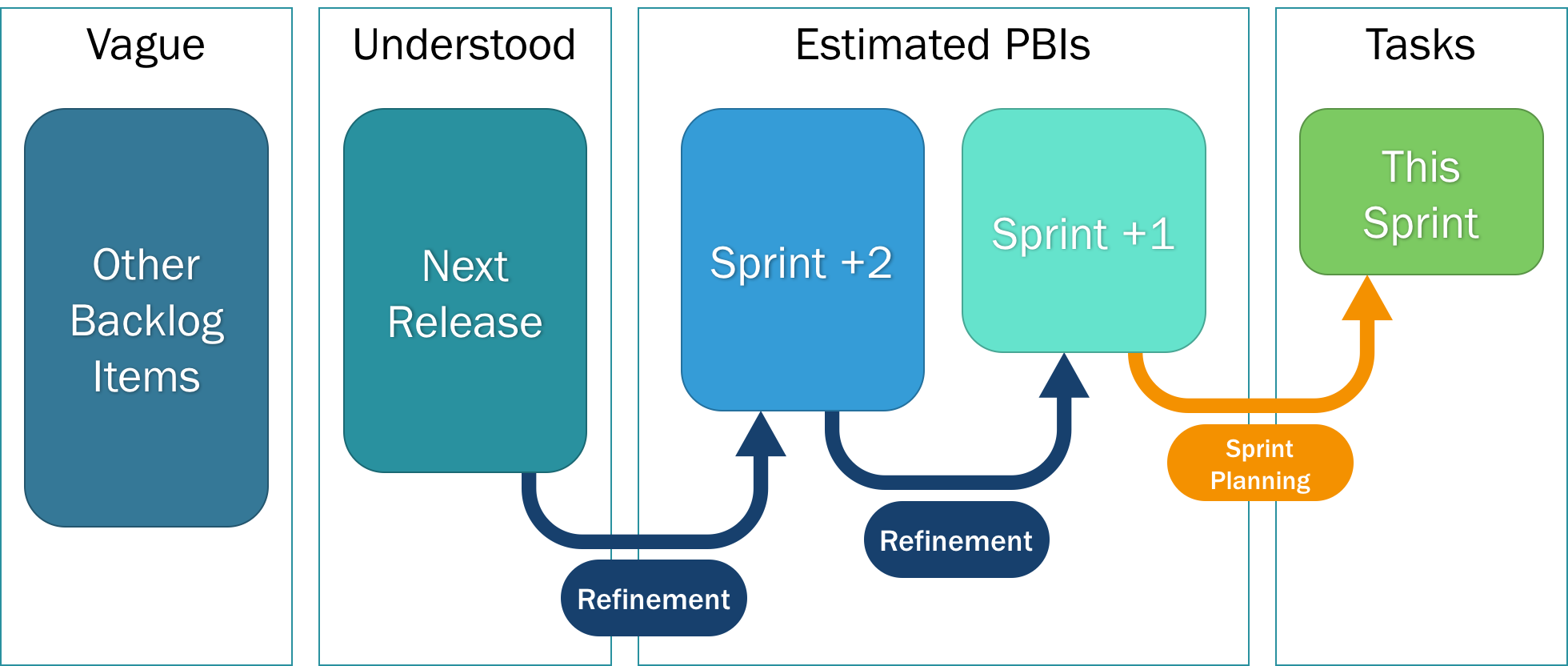
The work to be performed in the Sprint is planned at the Sprint Planning. This plan is created by the collaborative work of the entire Scrum Team.
Sprint Planning is time-boxed to a maximum of eight hours for a one-month Sprint. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter. The Scrum Master ensures that the event takes place and that attendants understand its purpose. The Scrum Master teaches the Scrum Team to keep it within the time-box.
Sprint Planning answers the following:
- What can be delivered in the Increment resulting from the upcoming Sprint?
- How will the work needed to deliver the Increment be achieved?
The Development Team works to forecast the functionality that will be developed during the Sprint. The Product Owner discusses the objective that the Sprint should achieve and the Product Backlog items that, if completed in the Sprint, would achieve the Sprint Goal. The entire Scrum Team collaborates on understanding the work of the Sprint.
By the end of the Sprint Planning, the Development Team should be able to explain to the Product Owner and Scrum Master how it intends to work as a self-organizing team to accomplish the Sprint Goal and create the anticipated Increment.
Figure 7: Sprint Planning Meeting
Daily Scrum
The Daily Scrum is a 15-minute time-boxed event for the Development Team to synchronize activities and create a plan for the next 24 hours. This is done by inspecting the work since the last Daily Scrum and forecasting the work that could be done before the next one. The Daily Scrum is held at the same time and place each day to reduce complexity.
The Development Team uses the Daily Scrum to inspect progress toward the Sprint Goal and to inspect how progress is trending toward completing the work in the Sprint Backlog. The Daily Scrum optimizes the probability that the Development Team will meet the Sprint Goal. Every day, the Development Team should understand how it intends to work together as a self-organizing team to accomplish the Sprint Goal and create the anticipated Increment by the end of the Sprint. The Development Team or team members often meet immediately after the Daily Scrum for detailed discussions, or to adapt, or replan, the rest of the Sprint’s work.
The Scrum Master ensures that the Development Team has the meeting, but the Development Team is responsible for conducting the Daily Scrum.
Daily Scrums improve communications, eliminate other meetings, identify impediments to development for removal, highlight and promote quick decision-making, and improve the Development Team’s level of knowledge. This is a key inspect and adapt meeting.
Sprint Review Meeting
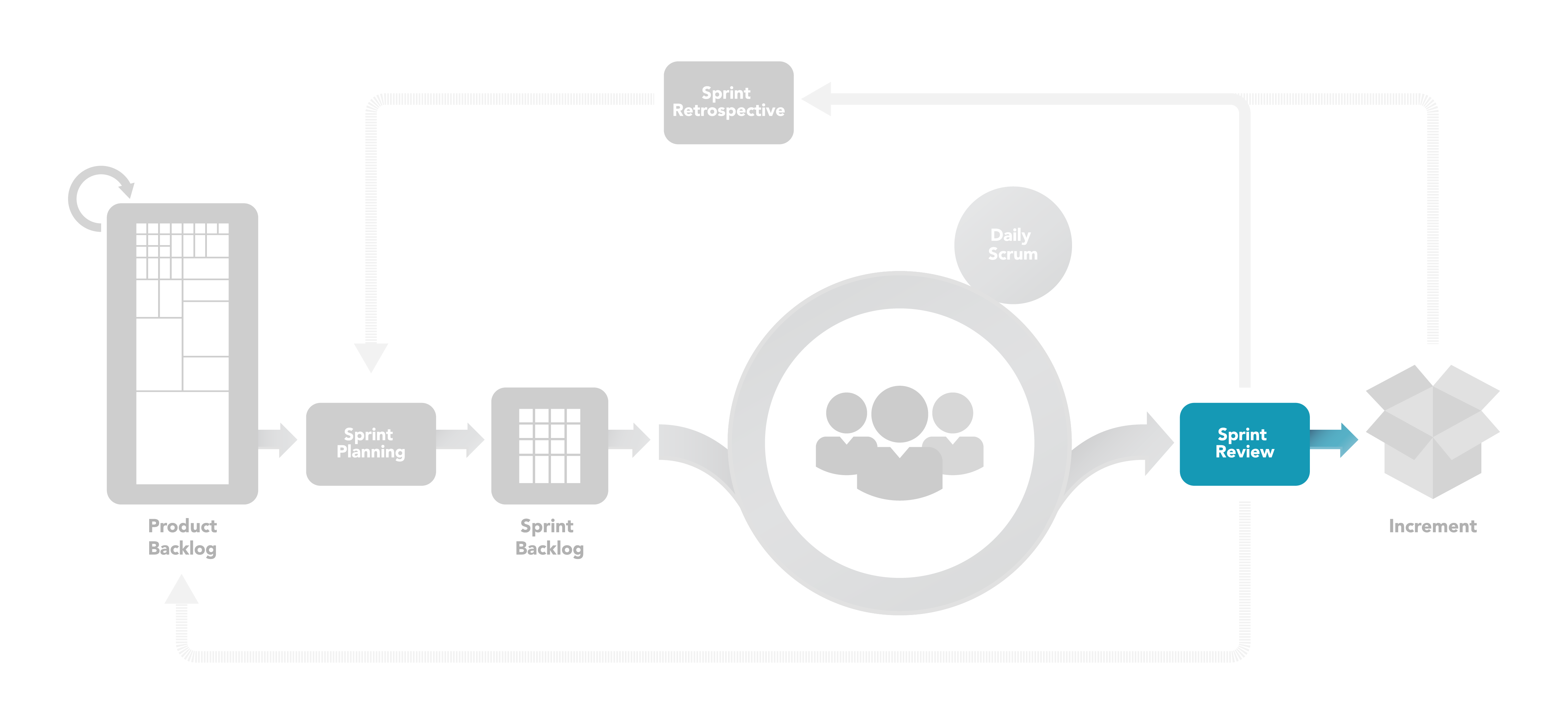
Development Teams deliver an Increment of product functionality at least every Sprint, but not limited to only once per Sprint. The Development Team may deliver an Increment more than once a Sprint. A Sprint Review is held at the end of the Sprint to inspect the Increment(s) and adapt the Product Backlog if needed. During the Sprint Review, the Scrum Team and stakeholders collaborate about what was done in the Sprint. Based on that, and any changes to the Product Backlog during the Sprint, attendees collaborate on the next things that could be done to optimize value. This is an informal meeting; not a status meeting, and not a phase gate before release. The presentation of the Increment is intended to elicit feedback and foster collaboration.
This is a four-hour time-boxed meeting for one-month Sprints. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter. The Scrum Master ensures that the event takes place and that attendants understand its purpose. The Scrum Master teaches all to keep it within the time-box.
The result of the Sprint Review is a revised Product Backlog that defines the probable Product Backlog items for the next Sprint. The Product Backlog may also be adjusted overall to meet new opportunities.
Figure 8: Sprint Review Meeting
Sprint Retrospective
The Sprint Retrospective is an opportunity for the Scrum Team to inspect itself and create a plan for improvements to be enacted during the next Sprint.
The Sprint Retrospective occurs after the Sprint Review and prior to the next Sprint Planning. This is a three-hour time-boxed meeting for one-month Sprints. For shorter Sprints, the event is usually shorter. The Scrum Master ensures that the event takes place and that attendants understand its purpose. The Scrum Master teaches all to keep it within the time-box. The Scrum Master participates as a peer team member in the meeting and has accountability over the Scrum process.
The purpose of the Sprint Retrospective is to:
- Inspect how the last Sprint went with regards to people, relationships, process, and tools;
- Identify and order the major items that went well and potential improvements; and,
- Create a plan for implementing improvements to the way the Scrum Team does its work.
The Scrum Master encourages the Scrum Team to improve, within the Scrum process framework, its development process and practices to make it more effective and enjoyable for the next Sprint. During each Sprint Retrospective, the Scrum Team plans ways to increase product quality by adapting the definition of “Done” as appropriate.
By the end of the Sprint Retrospective, the Scrum Team should have identified improvements that it will implement in the next Sprint. Implementing these improvements in the next Sprint is the adaptation to the inspection of the Scrum Team itself. Although improvements may be implemented at any time, the Sprint Retrospective provides a formal opportunity to focus on inspection and adaptation.




{{ parent.title || parent.header.title}}
{{ parent.tldr }}
{{ parent.linkDescription }}
{{ parent.urlSource.name }}